Let’s define Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) mirrors the actions of a human while performing a business process or task, but does it with more accurately , with quality, scalability, and speed. This functionality can be aligned to take over predictable and repetitive rule-based tasks with complicated steps. It can start a tool, operate it, work with data and do complex computations to deliver results. With maturity, RPA can also be used to perform decision-based tasks and communicate with other digital systems accordingly.
RPA is aligned with various business processes both front-end (customer assistance, filling out forms, etc.) and back-end (handling the completed forms, accounting, multiple computations, etc.)
RPA must be capable of performing data operations and analysis of structured data, as well as, process unstructured data like images, documents, and multi-modal data. It’s efficiency increases when coupled with Artificial Intelligence.
If RPA starts learning on its own, then it can be utilized to do many complex tasks where difficult decisions have to be taken on the go. Hence RPAs can be used in a more profound form, as it grows through its maturity level.
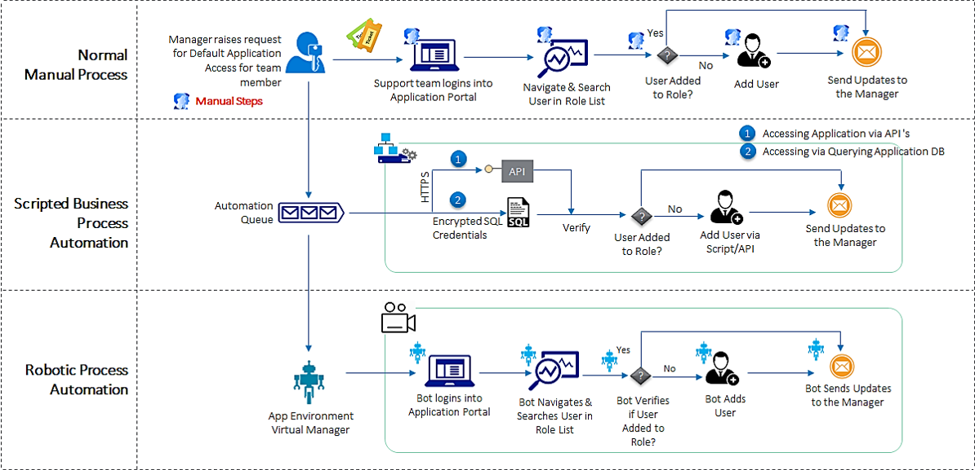
How does it work?
Let’s look at payroll processing, which is carried out once a week, bi-weekly or monthly depending on regulations and such. For a Global company with a specific payroll tool, it is not uncommon that some or few of the processes have to be carried out manually like uploading batch files from different sites concerning overtime or last minute earnings or deductions changes. This is a task that can be easily handled by RPA, saving time and money. An RPA system can be designed to handle any exception process flow or tasks withy any written set of instructions. The RPA system can also be given control to access the employee data, such as their stipulated cost to company and timesheets. Say the data is handwritten, RPA can also be instructed to extract that data, digitize and store it, before starting the payroll process. Using these data and the instructions given, it can either assist on feeding payroll with the pending information and if given control, it can further move forward and make the necessary bank transactions. And this process can be done in an unmatched speed for 24X7 hrs.
How is it built?
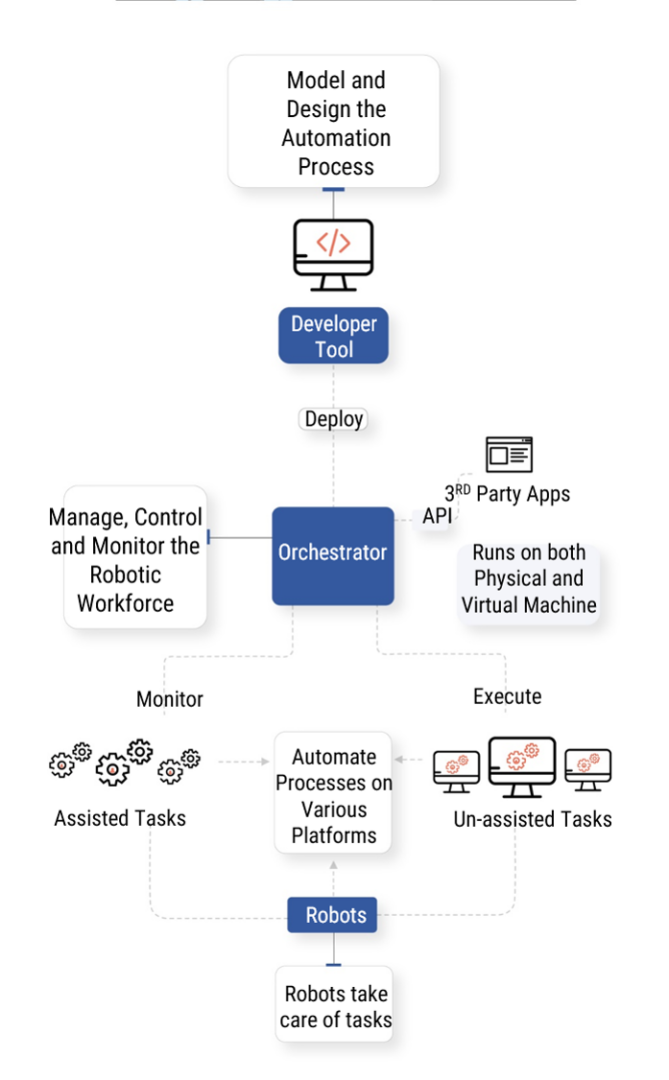
RPA broadly comprises three fundamental elements: a set of developer tools, a robot controller/orchestrator, and the software robots.
- Developer tools: Create a job workflow that a robot has to do, using these tools. Step-by-step instructions are written containing the detailed business logic and decision-based statements to complete the task journey. These tools are easy to use as some of them have drag and drop features with automatic configuration facilities. Some tools also feature ‘process recorder’ functionality that capture user actions in performing a task, and imitates the process. Complex processes of a task can also be visually represented, which are interactive.
- Robot Controller: This part has access to the master repository that contains all the jobs designed by the developer tools. The controller has all the credentials to access the different applications and provides the same to the robots while assigning tasks to each of them. It not only assigns and deploys jobs to the robots, but also provides an appropriate level of control to the robots and their users, along with updating, testing, and approving the jobs. It also audits, monitors and reports on each of the robots’ activities, along with release management, centralized logging, scheduling, workload and asset management.
- Software robots: They are the agents that do the work assigned to them, by the robot controller. These carry out the role of an automated assistant running efficiently, under supervision, or autonomously process all the high-volume work that does not require constant human intervention. They also keep a log detailing each of their actions. Compliances are taken care of using these logs, as well as; business heads can analyze them and make further improvements.
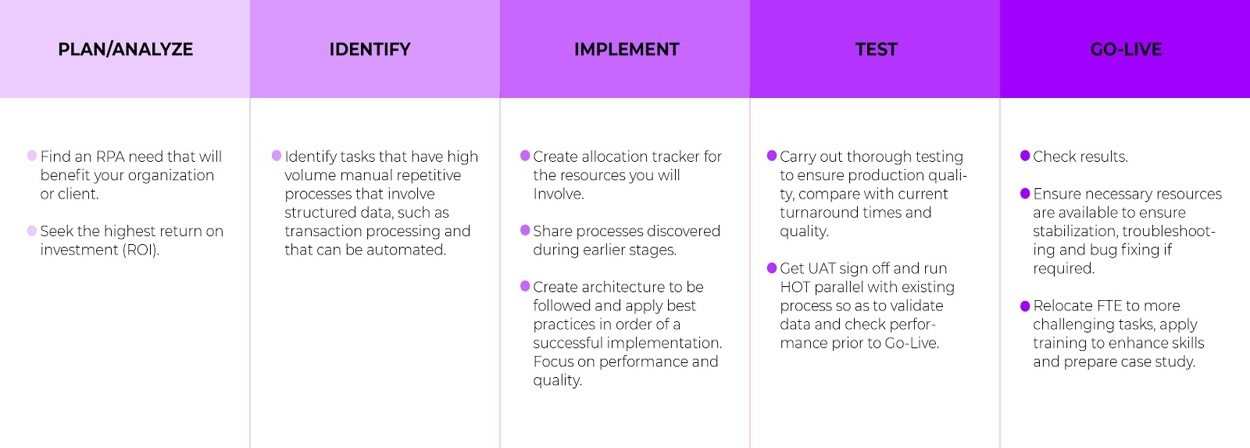
Implementation Methodology
 Case studies:
Case studies:
Globant using UIPath and BluePrism has automated and optimized banking operational processes for a number of leading banks.
As for example, for one bank, processes like updating client information, renewing insurance policies and card renewal/replacement which were earlier done in the traditional way have been automated. RPA robots are tasked with finding out new data on customers, and update them on relevant places. In insurance renewal, it fetches relevant data from various allocated sources, verifies them and if all the conditions are met, it proceeds to renew insurance policies automatically. The speed of the work and amount of transactions handled per day had a drastic change. Where the time taken to transact daily volume was around five and half hours; with RPA it decreased approximately one hour.
For another leading bank, using BluePrism, Globant has assisted in the KYC ‘Know Your Customer’ process. Through this process, banks can not only know about their customers and their respective financial dealing, but also prevent money laundering and swindling beforehand. This is an essential risk management process which is mostly done manually, but with RPA, this process not only increases in speed and volume but also decreases erroneous operations. RPA sped the process to almost 4.8 times to what was before.

For RPA related questions and assistance, please email stayrelevant@globant.com
Sources:
- https://mindmajix.com/30-rpa-examples
- https://www.uipath.com/blog/uipath-web-automation-see-exactly-how-rpa-magic-works
- https://www.uipath.com/platform
- http://blog.symphonyhq.com/what-is-rpa
- http://deloitte.wsj.com/cio/2016/03/13/an-introduction-to-robotic-process-automation/
- http://opensourceforu.com/2017/03/robotic-process-automation/
Image Courtesy:
- www.uipath.com
- www.blueprism.com



